Russia-Ukraine war—why did it begin, and how has it evolved into one of the most devastating conflicts of our time? What were the triggers that set this geopolitical crisis in motion, and where does the world stand today? When Russia launched its full-scale invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022, the global community watched in shock. What started as a regional dispute soon escalated into a major war, reshaping international relations, economies, and political alliances. As an Indian observer, I often wonder: What does this conflict mean for global stability, and where does India stand?
The Origins of the War: Why Did Russia Invade Ukraine?
To understand the Russia-Ukraine war, we must examine the deep-rooted historical, political, and strategic factors that led to the conflict.
1. Historical Context
Ukraine and Russia share a long history dating back to the medieval Kyivan Rus, which both nations consider their cultural ancestor. Over centuries, Ukraine was part of the Russian Empire and later the Soviet Union. When Ukraine declared independence in 1991 after the Soviet collapse, Russia struggled to accept its complete sovereignty.
2. NATO Expansion and Russian Opposition
One of Russia’s main grievances has been NATO’s eastward expansion. Since the 1990s, NATO has incorporated former Soviet states like Poland, Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia. Moscow viewed this as a direct threat to its security. Ukraine’s growing desire to join NATO further alarmed Russia, leading to tensions that culminated in the invasion.
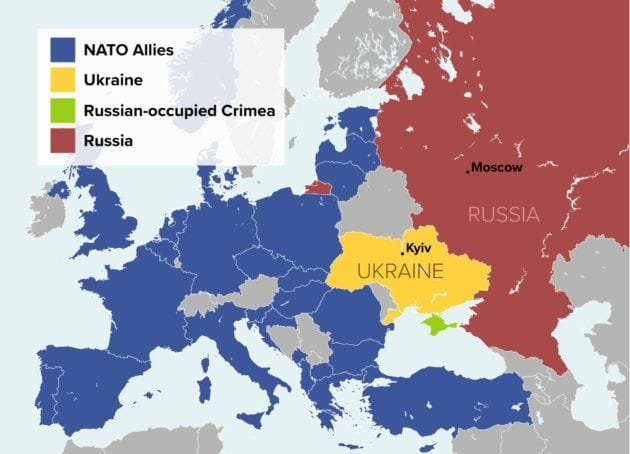
3. Annexation of Crimea (2014) and the Donbas Conflict
In 2014, Russia annexed Crimea following Ukraine’s pro-European Maidan Revolution. This move, condemned globally, led to Western sanctions. Simultaneously, Russian-backed separatists in Donetsk and Luhansk started an armed conflict against the Ukrainian government. The fighting continued for years, setting the stage for the 2022 invasion.
4. Economic and Political Tensions
Ukraine’s increasing economic ties with the European Union and its departure from Russia’s influence played a significant role. Russia saw Ukraine’s trade agreements with the EU as a move away from its sphere of influence. The Kremlin also accused the West of instigating regime changes in Ukraine to install a pro-Western government.
5. Military Buildup and Invasion
In late 2021 and early 2022, Russia amassed troops along Ukraine’s borders under the pretext of military drills. Despite diplomatic efforts, Russian President Vladimir Putin announced the invasion on February 24, 2022, citing the need to “demilitarise and denazify” Ukraine—claims widely dismissed as unfounded by global leaders.
Key Triggers of the War
| Factor | Explanation |
| NATO Expansion | Russia opposed Ukraine’s potential NATO membership, fearing Western military presence near its borders. |
| Crimea Annexation | In 2014, Russia annexed Crimea, escalating tensions and triggering Western sanctions. |
| Donbas Conflict | Pro-Russian separatists in Donetsk and Luhansk fought Ukrainian forces, with Russia providing military support. |
| Western Influence | Ukraine’s growing ties with the EU and NATO angered Moscow, which saw it as an erosion of Russian influence. |
| Military Build-up | Russia stationed thousands of troops near Ukraine’s borders before launching the full-scale invasion in 2022. |
India’s Stand on the Russia-Ukraine War
India has maintained a neutral stance, balancing its historic ties with Russia and its growing strategic partnerships with the West. This approach is guided by diplomatic pragmatism, economic considerations, and long-term geopolitical stability. India’s policy regarding the Russia-Ukraine war can be categorised into three main areas:
1. Diplomatic Neutrality and Strategic Balancing
India has avoided taking sides in the war, instead calling for diplomacy and peaceful resolution. This approach stems from its historical ties with Russia dating back to the Cold War era. India has urged both Russia and Ukraine to engage in dialogue while refraining from directly condemning Moscow.
- UN Votes: India has abstained from multiple UN resolutions condemning Russia’s actions. This abstention aligns with India’s principle of non-interference in internal conflicts.
- Bilateral Relations: Despite Western pressure, India has maintained strong diplomatic ties with Russia while also strengthening its relationships with the U.S. and European nations.
2. Economic Considerations: Oil, Trade, and Sanctions
One of the major reasons behind India’s neutral stance is its economic interests, particularly in energy security. Russia has been a crucial supplier of discounted oil to India, helping it manage inflation and energy costs.
- Oil Imports: India has significantly increased its imports of Russian crude oil since the war began, taking advantage of lower prices.
- Trade Relations: Bilateral trade between India and Russia has grown despite global sanctions, covering sectors such as defense, pharmaceuticals, and fertilizers.
Western Pressure and Response: The U.S. and EU have urged India to reduce dependence on Russian energy, but India has defended its purchases as a matter of national interest.
3. Defense and Security Ties with Russia
India relies heavily on Russian military equipment, which has been a crucial factor in its stance. Nearly 60% of India’s defense hardware comes from Russia, including fighter jets, submarines, and missile systems.
- Dependence on Russian Arms: India’s military modernisation efforts still involve major Russian technologies, making it difficult to sever ties.
- Diversification Efforts: While India has started diversifying its arms imports by strengthening defense partnerships with the U.S., France, and Israel, it still values its defense ties with Moscow.
4. Humanitarian Concerns and Indian Citizens
India has expressed deep concern over the humanitarian crisis caused by the war, particularly the safety of its citizens studying and working in Ukraine.
- Operation Ganga: The Indian government launched a large-scale evacuation mission to bring back thousands of Indian students stranded in Ukraine during the early days of the war.
- Humanitarian Aid: India has sent medical supplies and humanitarian assistance to Ukraine while maintaining diplomatic engagement with both sides.
5. The Geopolitical Implications for India
The war has broader implications for India’s strategic positioning on the global stage.
- Balancing the West and Russia: India’s stand has reinforced its image as an independent global player that prioritizes national interests over aligning with any single bloc.
- China Factor: India is cautious about pushing Russia closer to China, given its own security concerns with Beijing. Keeping Moscow as a strategic partner helps India counterbalance China’s growing influence.
India’s Position in Key Aspects of the Conflict
| Aspect | India’s Approach & Stance |
| UN Resolutions | India has abstained from voting against Russia but supports calls for peaceful resolution. |
| Diplomatic Engagements | India has maintained open dialogue with both Russia and Ukraine, advocating for ceasefire talks. |
| Energy Security | India continues importing Russian oil at discounted rates to counter global inflation. |
| Defense Ties | India remains a major buyer of Russian defense equipment while diversifying its defense partnerships. |
| Trade Relations | Bilateral trade with Russia has increased, especially in energy and fertilizers. |
| Humanitarian Aid | India has sent medical aid and relief supplies to Ukraine, demonstrating support for humanitarian efforts. |
| Western Pressure | India has resisted Western calls to sanction Russia, maintaining a neutral stance. |
The World’s Stand on the Russia-Ukraine War
The Russia-Ukraine war has had far-reaching consequences, extending beyond the borders of these two nations. This war has reshaped international economic structures, altered diplomatic alliances, and brought about global instability in multiple ways.
The West: Firm Opposition and Military Support
The United States and its European allies have been the most vocal in condemning Russia’s invasion. Western nations have backed Ukraine both militarily and economically, emphasizing the importance of defending democracy and maintaining regional stability.
Military Assistance
The U.S. has emerged as Ukraine’s primary military backer, supplying a range of advanced weaponry, including:
- The U.S. has emerged as Ukraine’s primary military backer, supplying a range of advanced weaponry, including:
- HIMARS rocket systems: Providing Ukraine with extended-range precision strikes.
- Patriot missile defense systems: Strengthening Ukraine’s air defense against Russian aerial assaults.
- Tanks and armored vehicles: Facilitating counteroffensive operations against Russian-occupied territories.
- Drones and surveillance technology: Enhancing Ukraine’s reconnaissance capabilities
NATO, while refraining from direct military involvement, has reinforced its eastern flank with additional troop deployments in Poland, Romania, and the Baltic states to deter any potential Russian aggression beyond Ukraine.
Economic Sanctions Against Russia
The West has launched an economic offensive against Russia, aiming to cripple its war-funding capabilities:
- Energy Restrictions: The EU has drastically reduced its dependence on Russian oil and gas, imposing import bans and exploring alternative energy sources.
- Financial Sanctions: Russian banks have been cut off from the SWIFT system, restricting international transactions.
- Asset Freezes: The West has seized billions in Russian assets, including those of oligarchs close to the Kremlin.
- Trade Embargoes: Restrictions have been placed on high-tech exports, including semiconductors and aviation parts, to hinder Russia’s military production.
Despite these measures, Russia has managed to find workarounds, leveraging alternative financial systems and trade with China, India, and Middle Eastern nations.
Diplomatic Stance
European leaders are increasingly wary of peace talks that may favor Russia. They emphasize that any resolution must respect Ukraine’s sovereignty and territorial integrity. However, disagreements persist within the EU, with some nations, like Hungary, advocating for immediate negotiations, while others, like Poland and the Baltic states, push for continued military aid to ensure Ukraine’s victory.
The U.S. has taken a firm stance, stating that negotiations should be led by Ukraine without external pressures. However, with a change in administration, there have been hints of possible diplomatic engagements between Washington and Moscow
Global Impact Breakdown
| Impact Area | Effects on India and the World |
| Oil Prices | Surge in crude oil prices affected fuel costs worldwide, including India, leading to inflationary pressures. |
| Food Security | Ukraine and Russia being major grain exporters, supply chain disruptions led to global food inflation, affecting developing nations the most. |
| Supply Chains | Disruptions in transportation routes and export bans led to shortages of key commodities like fertilisers and semiconductors. |
| Geopolitical Tensions | Strengthened alliances between the West and Ukraine, while Russia deepened ties with China, Iran, and North Korea, altering global diplomatic relations. |
| Defense Spending | Countries worldwide, including India, have increased military budgets, investing in advanced weaponry and cybersecurity. |
| Refugee Crisis | Over 10 million displaced Ukrainians, primarily in Europe, straining humanitarian aid and resources. |
| Cybersecurity Threats | Rise in cyber warfare tactics, affecting global financial institutions, government agencies, and communication networks. |
| Sanctions and Trade | Western sanctions on Russia impacted global trade routes, affecting industries that relied on Russian raw materials and energy. |
| To understand the historical and geopolitical complexities of the Russia-Ukraine conflict, here are some insightful books that provide deep analysis and context: 📖 RUSSIA: REVOLUTION AND CIVIL WAR 1917-1921 – Explore the turbulent history of Russia’s revolution and civil war, which laid the groundwork for many of the geopolitical tensions seen today. 📖 New Cold Wars – This book examines how global power struggles, including the Russia-Ukraine crisis, have reignited Cold War dynamics in the modern world. 📖 How the West Brought War to Ukraine – A thought-provoking take on the role of Western policies in shaping Ukraine’s conflict with Russia. 📖 War – A deep dive into the nature of war itself, providing a broader understanding of military conflicts, including the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war. |
Russia’s Justification and Alliances
Moscow continues to justify its actions as a response to NATO’s expansion and Ukraine’s alleged threats to Russian-speaking populations in Donbas. Despite global condemnation, Russia has found allies or at least neutral parties:
- NATO Expansion and Security Concerns: One of Russia’s key arguments for the invasion is its longstanding opposition to NATO’s eastward expansion. Russia has repeatedly stated that NATO’s inclusion of Ukraine would pose a direct threat to its national security, claiming that Western powers have ignored its security concerns.
- Protection of Russian-Speaking Populations: The Kremlin has frequently asserted that its military operation was necessary to protect Russian-speaking communities in Donetsk and Luhansk, which it claims have been subjected to discrimination and violence by Ukrainian forces. This justification has been widely dismissed by Western nations as a pretext for aggression.
- Strategic Alliances: Despite being widely condemned, Russia has found support—both open and tacit—from a few key nations:
- China’s Position: While Beijing has not openly supported Russia’s invasion, it has refrained from condemning it. China has maintained trade ties, opposed Western sanctions, and increased its economic cooperation with Russia, ensuring that Moscow does not become completely isolated.
- Iran and North Korea: These nations have played a more direct role in aiding Russia. Reports suggest that Iran has supplied drones and other military equipment, while North Korea has provided artillery shells and other munitions to bolster Russia’s military campaign.
- Middle East’s Stance: Countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE have attempted to mediate peace but have also continued energy cooperation with Russia. OPEC+ decisions, heavily influenced by Russia, have played a role in stabilizing global oil prices in Moscow’s favor.
- Russia’s Economic Resilience: Despite severe sanctions, Russia has managed to sustain its economy through alternative trade partnerships. Increased trade with China, India, and other Asian economies has allowed Russia to bypass many Western restrictions, keeping its war efforts funded.
- Military and Diplomatic Maneuvering: Russia has continued to project strength through military alliances, including participation in joint military exercises with China and Belarus. Furthermore, Moscow has leveraged diplomatic ties with African and Latin American countries to counteract Western narratives on the war.
Peace Talks and Future Scenarios
Several diplomatic efforts have been made to end the conflict, but achieving a sustainable peace remains uncertain:
- Saudi Arabia’s Mediation Efforts: The U.S. and Russia have held talks in Saudi Arabia, but Ukraine was notably absent from these negotiations.
- European Leaders’ Concerns: European nations fear that rushed peace talks may lead to a deal that favours Russia, leaving Ukraine at a strategic disadvantage.
- Ukraine’s Position: Kyiv has consistently rejected peace settlements that compromise its territorial integrity, pushing instead for a complete Russian withdrawal.
- Possible Future Scenarios:
- Prolonged Conflict: The war could continue for years, leading to ongoing economic and humanitarian devastation.
- Negotiated Peace: A ceasefire could be reached, but long-term peace will require addressing security concerns on both sides.
- Military Victory: Either Ukraine or Russia could achieve a decisive victory, reshaping the geopolitical order in Europe
Conclusion
The Russia-Ukraine war is not just a regional conflict—it has transformed global political, economic, and security landscapes. It has intensified geopolitical rivalries, strengthened alliances, and reshaped global trade dynamics. The conflict has exposed vulnerabilities in the global economy, from soaring energy prices to supply chain disruptions, affecting countries far beyond Europe. It has also set a precedent for international conflicts, where military aggression challenges established global norms.
For India, the war has highlighted the importance of maintaining a delicate diplomatic balance. While India has maintained strong historical ties with Russia, it has also deepened economic and strategic partnerships with Western nations. This balancing act reflects India’s commitment to a multipolar world where national interests guide foreign policy rather than alignment with any single power bloc.
Looking ahead, the war’s outcome will shape future international relations. A prolonged conflict could deepen divisions between major world powers, while a peaceful resolution—though currently unlikely—could lead to a new framework for global diplomacy. Regardless of how it ends, the Russia-Ukraine war will have long-term implications for global security, economic stability, and political alliances, ensuring that its effects will be felt for decades to come.
📢 Share this article with your friends and family to keep them informed!
🔍 Explore More: https://thinkingthorough.com
📩 Let’s Connect: Have thoughts or suggestions? Drop us a message on our social media handles. We will be waiting to hear from you!!
References
Jazeera, A. (2025, February 13). European leaders seek seat in Ukraine peace talks after Trump calls Putin. Al Jazeera. https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2025/2/13/european-leaders-seek-seat-in-ukraine-peace-talks-after-trump-calls-putin
BBC News. (2025b, February 17). Ukraine war talks: What the key players want. https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cwypy119yzno
Ray, & Michael. (2025, February 27). Russia-Ukraine War | Casualties, Map, Causes, & Significance. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/event/2022-Russian-invasion-of-Ukraine
Q2: How does this war affect India’s economy?
India has both challenges and opportunities stemming from the conflict. On the one hand, rising fuel prices have impacted inflation and increased costs for industries dependent on crude oil. On the other hand, India has been able to secure discounted Russian oil, helping to stabilize its energy security. Additionally, disruptions in global supply chains have affected semiconductor availability, increasing production costs for tech industries.
Q3: Can India mediate peace talks?
India’s strong diplomatic relations with both Russia and the West make it a potential mediator. However, neither Ukraine nor Russia has expressed serious interest in third-party mediation at this stage. While India has called for peaceful resolution, the deep-rooted mistrust between the two warring nations remains a significant obstacle.
Q4: What has been the role of the West in the war?
The West, particularly the U.S. and EU, has played a crucial role in supporting Ukraine through military aid, economic sanctions against Russia, and diplomatic backing. The ongoing supply of advanced weaponry and economic measures has helped Ukraine sustain its resistance while putting financial pressure on Russia.
Q5: What is the humanitarian situation in Ukraine?
The humanitarian crisis is dire, with millions of displaced people, destroyed infrastructure, and widespread war crimes allegations. Organizations such as the United Nations and Red Cross are working to provide aid, but access to conflict zones remains limited. The war has also triggered a massive refugee crisis, with many Ukrainians seeking asylum in neighbouring countries.
